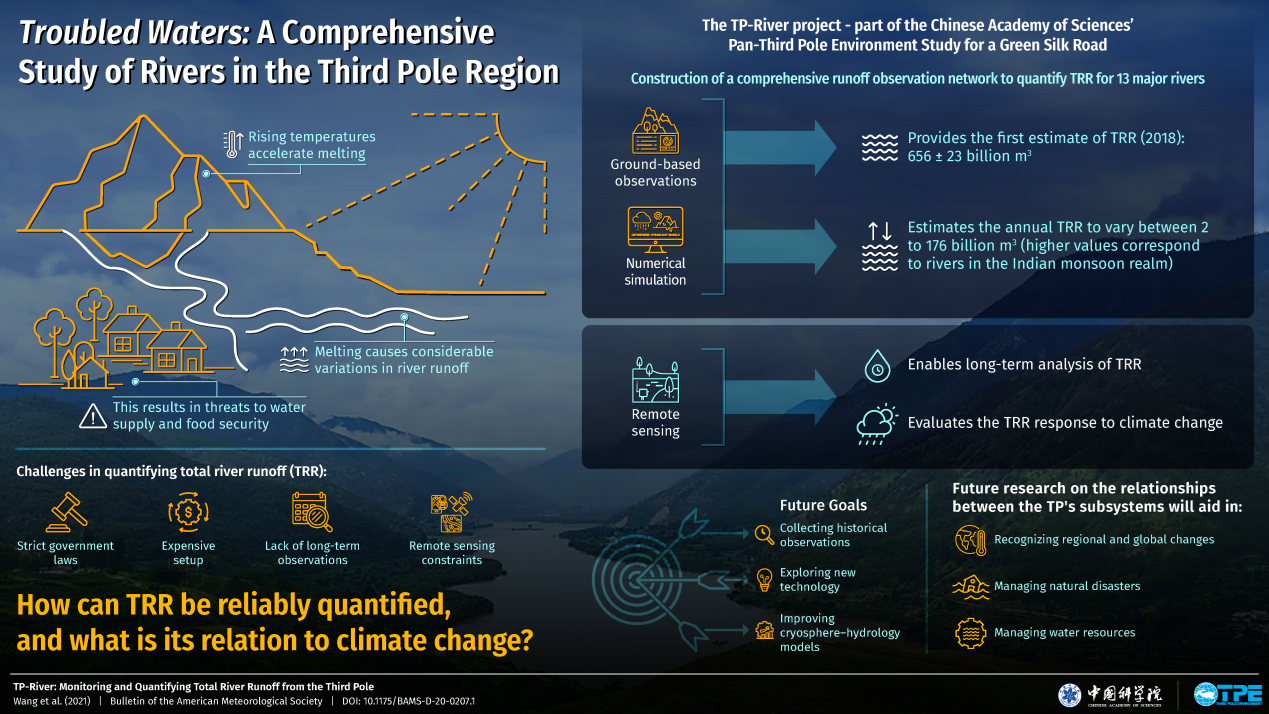
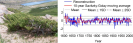
The Third Pole centered on the Tibetan Plateau is home to the headwaters of over 10 major Asian rivers. Despite the importance of these rivers, how much water flows out of the mountains of the Third Pole as river runoff is not known by scientists yet. Now, however, researchers from the Institute of Tibetan Plateau Research (ITP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have quantified the total river runoff of 13 major rivers in the region.
 2021-07-05
2021-07-05
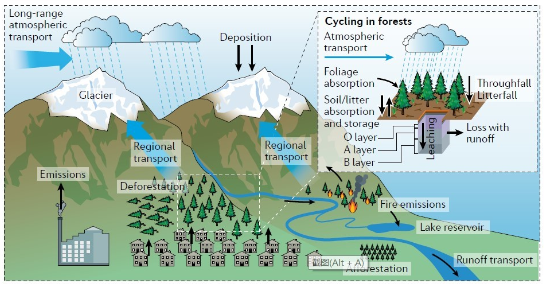
As a part of the global material flow , the global dispersion of persistent organic pollutants ( POPs ) is also regulated by forests .In theory , the forest plays as a " sink " and delays the transport of POPs to remote/cold regions .For example , from a global perspective , what is the distribution of POPs in forests ? How will forest changes influence the global transport of POPs ? To answer these questions , Dr . Ping Gong from the Institute of Tibetan Plateau Research .
 2021-03-04
2021-03-04
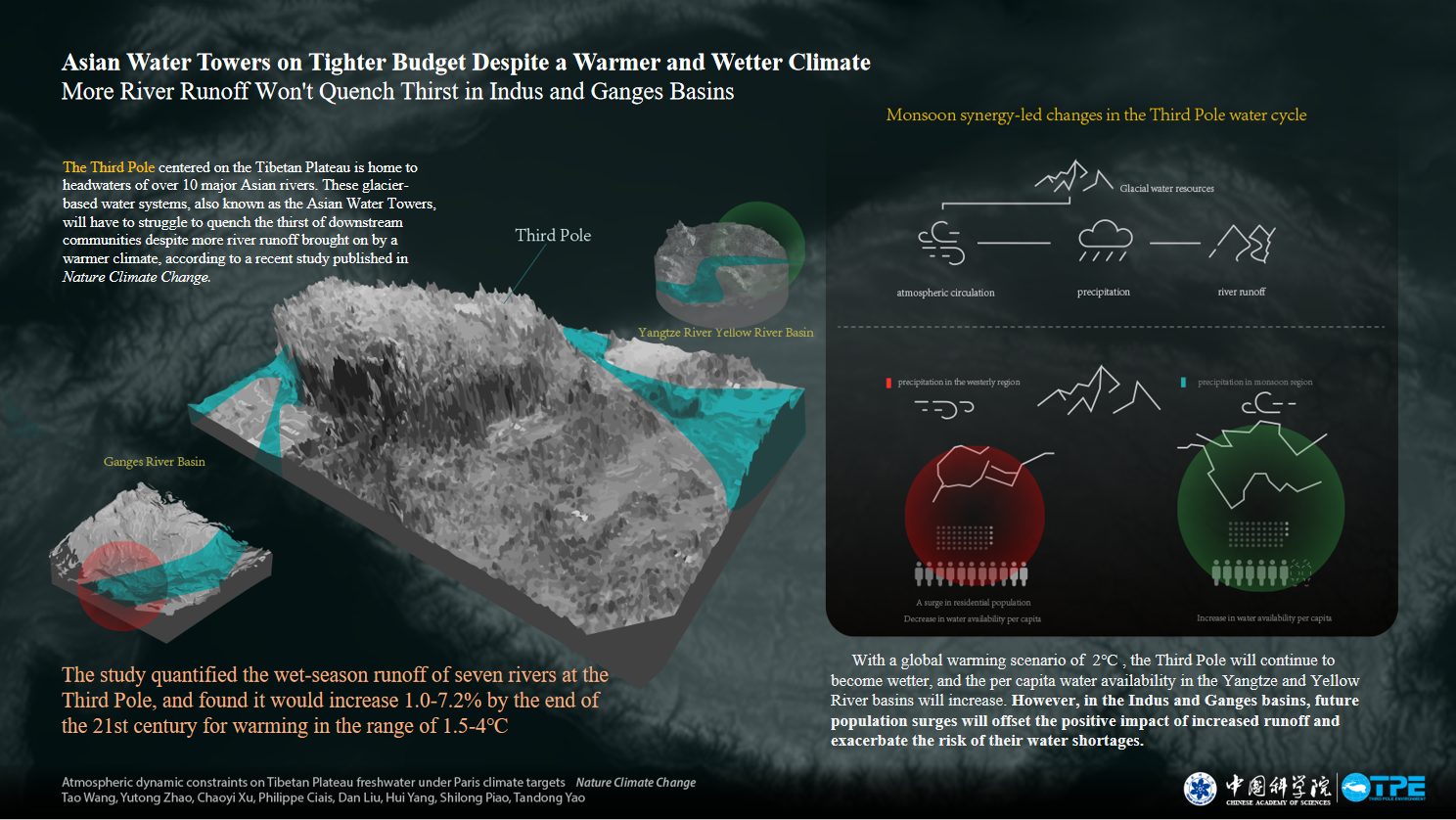
 2021-01-13
2021-01-13

As the roof of the world , the Third Pole centered on the Tibetan Plateau can be easily considered a permanent presence .” pointed out by Fang , referring to the findings of the First Tibetan Plateau Expedition and Research ( FTEP ) , which was carried out ? in 1970s as the first large scale scientific expedition ? focusing on the Third Pole .With this recalibrated elevation history , there is still much work to do in the future . ? https : / / advances . sciencemag . org/content / 6 / 50 / eaba7298 ? ? ?.
 2020-12-10
2020-12-10
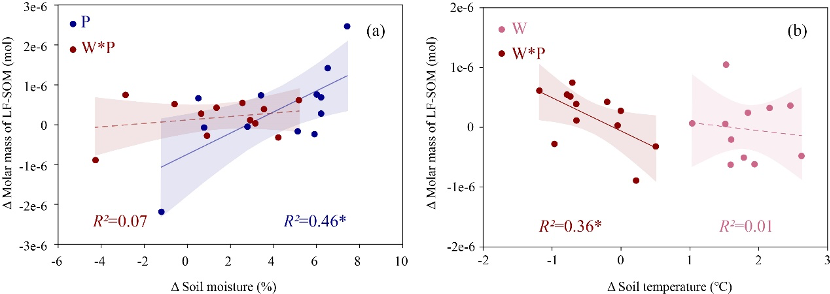
Soils on the Tibetan Plateau are extremely sensitive to global climate change .The lack of understanding of soil organic matter ( SOM ) transformation processes in this region hinders the prediction of SOM stocks under future climate conditions .Recently , Prof . Gengxin Zhang ’ s group of Institute of Tibetan Plateau Research , Chinese Academy of Sciences studied the responses of the alpine SOM to global climate change , including Nitrogen ( N ) deposition , warming and increased precipitation .
 2020-06-24
2020-06-24
The Nam Co , situated within the south-central Tibetan Plateau ( 30 ° – 35 ° N ) , is located at the transitional region between the Indian summer monsoon and westerlies in the growing season .This area with an elevation above 4700 m a . s . l . is characterized by extremely cold and dry treeless environment .Among alpine shrubs , Wilson juniper ( Juniperus pingii var . wilsonii ) is widespread throughout the south-central Tibetan Plateau . ?.
 2020-06-23
2020-06-23
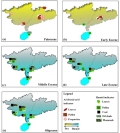
The modern environment of southern China is dominated by a humid monsoon climate , and presents a striking contrast to the widespread deserts found at similar latitudes elsewhere .Comparison of Paleogene palynological records of southern China , with global climate change expressed by deep-sea δ 18O records ( modified from Zachos et al . , and tectonic events ( Wang et al . .
 2020-05-09
2020-05-09
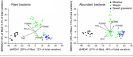
The rare biosphere contains microorganisms that present in low abundance .These rare microorganisms represent the majority of the Earth ' s biodiversity and are responsible for ecosystem multifunctionality and act as the “ seed bank ” during ecological restoration .However , the diversity and biogeography of rare microorganisms are still poorly understood in the terrestrial ecosystem .Fig . 4 Correlations between the community composition and phylogeny for rare and abundant bacteria ?.
 2020-05-08
2020-05-08
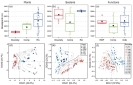
Although biodiversity and ecosystem functions are strongly shaped by contemporary environments , such as climate , local biotic and abiotic attributes , we know relatively little about how they change along with long-term geological processes .The integration of geological processes with environmental gradients could enhance our understanding of biodiversity and ecosystem functioning across different climatic zones . ? ? Further studies are encouraged to study the legacies of past geological events on biological communities and ecosystem functions .
 2020-04-15
2020-04-15
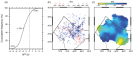
Chinese Academy of Sciences has led a study to image the small-scale structure of the D ' ' layer beneath the India-Eurasian plate collision zone . ? ? This study is mainly based on the waveform data of eight earthquakes in the Indian Ocean recorded by the dense China Digital Seismic Network ( Figure 1b ) .The median value of δ t3D is - 1.75 s and 95% of the values fall between - 4.57 s and + 1.63 s . ( b ) Values of dVs plotted at the CMB reflection points of ScS . ( c ) Map of dVs after cap smoothing using caps with radii of 2o and cap centers spaced every 0.5o .
 2020-03-23
2020-03-23